✦+
+
What's vulvovaginal candidiasis?
Vulvovaginal candidiasis, also called vaginal yeast infection is a fungal infection that causes irritation, discharge and intense itchiness of the vagina and the vulva — the tissues at the vaginal opening.Vulvovaginal candidiasis, bacterial vaginosis, and trichomoniasis are the most common cause of vaginitis of which vulvovaginal candidiasis is the second most common after bacterial vaginosis. Nearly 5–10 million females seek gynecologic advice for vaginitis every year world-wide.Many studies have reported that three fourth (75%) of women will experience an episode of vulvovaginal candidiasis in their lifetimes, 50% of these will experience at least a second episode, and 5–10% of all women experience recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis.
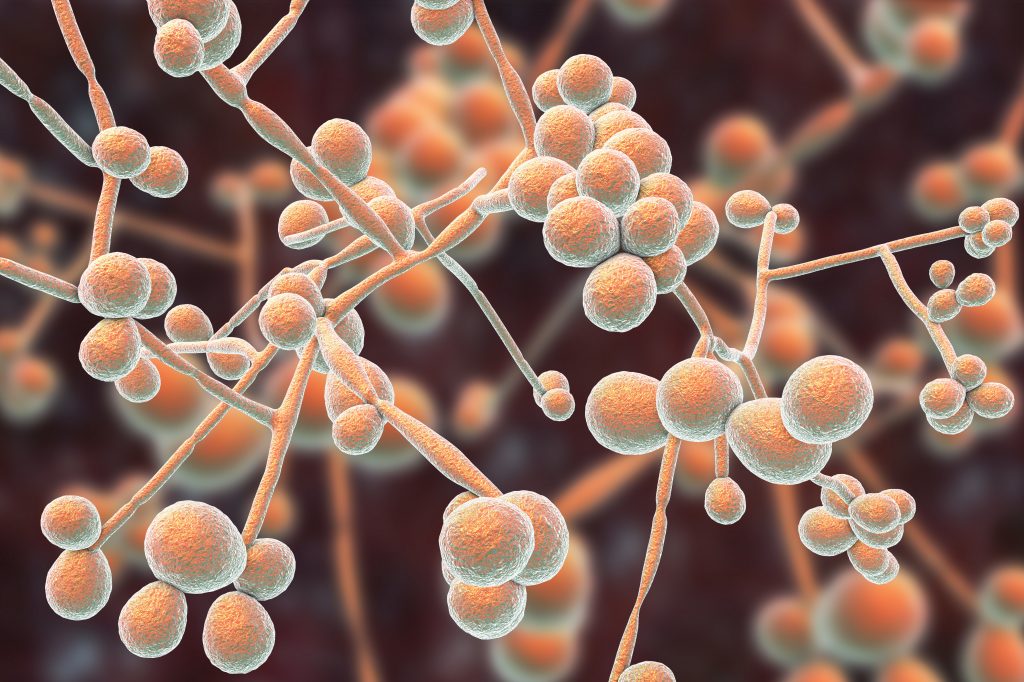
Source: https://www.dtapclinic.com/
✦+
+
Symptom
Yeast infection symptoms can range from mild to moderate, and include:
🔹Itching and irritation in the vagina and vulva;
🔹 A burning sensation, especially during intercourse or while urinating;
🔹 Redness and swelling of the vulva;
🔹 Vaginal pain and soreness;
🔹 Vaginal rash;
🔹Thick, white, odor-free vaginal discharge with a cottage cheese appearance;
🔹Watery vaginal discharge;
✦+
+
Cause
In women of child-bearing age, yeast infections due to Candida albicans are particularly common. This yeast normally resides on the skin or in the intestine. From these areas, it can spread to the vagina. Yeast infections are not transmitted sexually. Vaginal yeast infections are more likely to occur in women who
🔗 Are pregnant
🔗 Have diabetes
🔗 Have a weakened immune system—suppressed by drugs (such as corticosteroids or chemotherapy drugs) or impaired by a disorder (such as AIDS)
🔗 Use an intrauterine device
🔗 Wear tight undergarments that do not let air circulate
🔗 Are taking antibiotics
Antibiotics taken by mouth tend to kill the bacteria that normally reside in the vagina and that prevent yeast from growing. Thus, using antibiotics increases the risk of developing a yeast infection.

Source: https://www.afcurgentcarefountaincitytn.com/
✦+
+
Risk factor
Factors that increase risk of developing a yeast infection include:
⭕ Antibiotic use. Yeast infections are common in women who take antibiotics. Broad-spectrum antibiotics, which kill a range of bacteria, also kill healthy bacteria in your vagina, leading to overgrowth of yeast.
⭕ Increased estrogen levels. Yeast infections are more common in women with higher estrogen levels — such as pregnant women or women taking high-dose estrogen birth control pills or estrogen hormone therapy.
⭕ Uncontrolled diabetes. Women with poorly controlled blood sugar are at greater risk of yeast infections than women with well-controlled blood sugar.
⭕ Impaired immune system. Women with lowered immunity — such as from corticosteroid therapy or HIV infection — are more likely to get yeast infections.

Source: https://www.flickr.com/
✦+
+
Prevention
To reduce risk of vaginal yeast infections, wear underwear that has a cotton crotch and doesn't fit too tightly. It might also help to avoid:
🔘 Tight-fitting pantyhose;
🔘 Douching, which removes some of the normal bacteria in the vagina that protect you from infection;
🔘 Scented feminine products, including bubble bath, pads and tampons;
🔘 Hot tubs and very hot baths;
🔘 Unnecessary antibiotic use, such as for colds or other viral infections;
🔘 Staying in wet clothes, such as swimsuits and workout attire, for long periods of time;

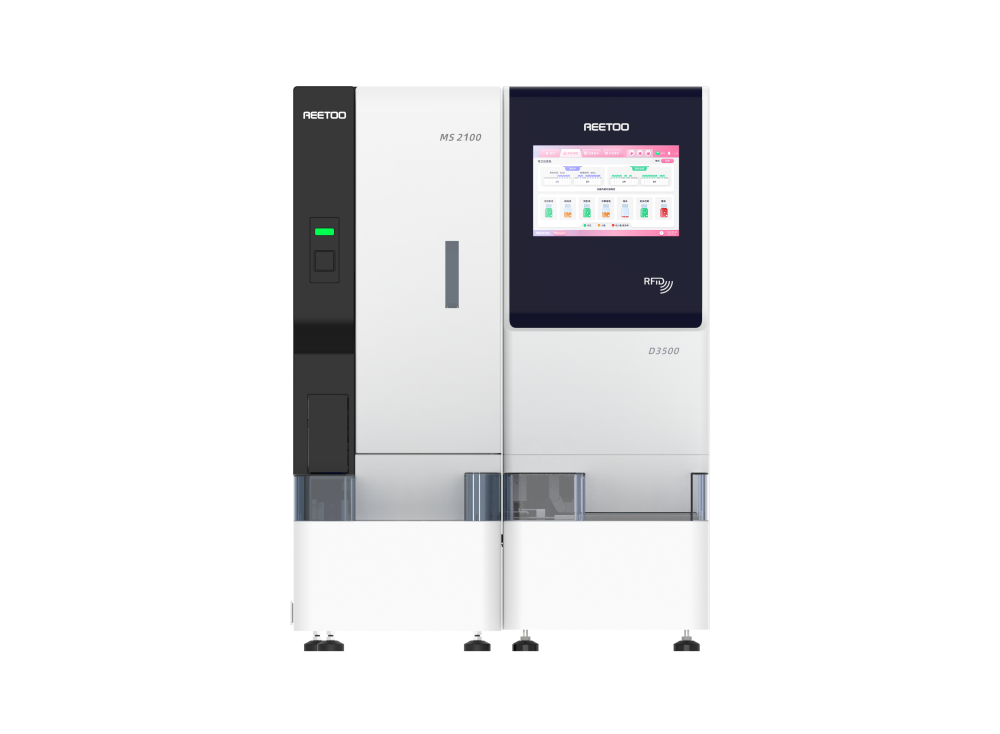
RT-F600: Vaginal Secretion Analyzer
✦+
+
Diagnosis
Key features:
✔ High speed: 40T/H;
✔ Cell recognition accuracy is up to 90%;
✔ Multi-layers dynamic focus scanning;
✔ Integrated test for microscopy and dry chemistry;
✔ Patent algorithm for tracking and recognizing trichomonas morphology;
+ + + + + + + + + + +
References:
+ + + + +


















 粤公网安备44030002003406
粤公网安备44030002003406